We have all heard people say that nanotechnology is the future of our generation and that future has already started to fulfill itself with silver nanoparticles. Silver has been known to have antimicrobial properties since the ancient Phoenicians started using silver vessels to store their drinking water. According to the article “Silver Tongues,” silver nanoparticles may become the next potent bactericide. The nanoparticles may be used in future clothes, soap, and even chopsticks in order to prevent germs. However, silver in large quantities can prove harmful and toxic; therefore, more research is underway on the silver and nanoparticles themselves, which can react in many different, possibly unsafe, ways. The germ killing ability of silver to be antimicrobial is obtained from its slow release of ions; when silver is produced in nanometers it sheds more ions and becomes more potent. The EPA (environmental protection agency) is up in arms about the large number of silver nanoparticle products like the “silver wash” a new washing machine that will clean clothes by releasing hundreds of billions of silver nanoparticles. EPA is worried about the environmental safety because the silver nanoparticles have no been tested extensively; they want the new products to be labeled as pesticides and regulated. A risk of silver nanoparticles is that the particles are so tiny that they may go into an organism and release their ions inside of it; silver’s ability to do this is the reason it is so affective, yet if silver starts releasing its ions into humans scientists are not sure how tolerant we would be to the new product. However, taking the risks into count, many scientists believe that there is great potential for the new silver nanoparticles to be used in medical equipment or in clothes to make them sterile; the EPA is still very determined to make the silver known as a pesticide to regulate the usage until further tests are developed.
Thursday, June 30, 2011
Wednesday, June 29, 2011
Water shortage vs water pollution
In the debate between wether water shortage or water pollution, water pollution is worse because there is plenty of water on Earth, yet there is barely any water available to drink. There is 1 % of fresh water is accessible to most human beings. The problem is that there are 6.4 billion people on this Earth and water, an essential source of life, is being taken away from most of them by big corporations like Suez and nestle. Many people around the world unfortunately do not have clean water to drink and become sick by drinking the only water source available to them; many of the ponds, rivers, or lakes that are around for people to drink or bath from may be contaminated with disease or even fecal matter. Though water shortage is a large problem in the world, water pollution is a more pressing problem because without fresh water and the resources to freshen the water many people will end up dying in the very near future. 3.575 million people die from water born diseases each year; however, the sad fact is that most of those diseases are curable. Because water is such a valuable resource everyone has to pay for their water, yet many people in poorer countries do not have enough resources to pay for their water and are forced into drinking the contaminated water that makes them sick. 1 out of every 8 people lack safe drinking water and people living in poor areas often pay more for their water than the richer people living in their same community. Water should be a clean, available resource to everyone, yet many people are suffering due to the unsafe water that is available to them.
Tuesday, June 28, 2011
Homework #2 week three
- On paper
- Three major processes that occur in natural water purification:
- Evaporation- evaporation is due to the heat from the sun’s rays that hit bodies of water. Evaporation acts like distillation because after the water evaporates the heavy metals and other the water leaves behind undesirable particles; the particles have higher evaporation points than water does.
- Bacterial action- bacterial action converts dissolved organic contaminants into a few simple compounds that are not harmful.
- Filtration- filtration through sand and gravel filters most suspended particles as well as the bacteria that clean the water.
- Aluminum hydroxide is related to the process of flocculation because the sticky property of the substance adsorbs unwanted particles and sinks to the bottom of the water tanks as sludge, which then allows the top layer of cleaner water to be taken and filtered again through sand.
- Calcium oxide is sometimes added in the final step of municipal water treatment because it needs to neutralize the pH of water that may have turned to acidic. Acidic water deteriorates the pipes, which then allows Copper and Cadmium into the water making it unsafe to drink.
- Fluoride is added to some water in the final stage of the purification process in order to reduce tooth decay; however, only 1ppm of fluoride maybe be present in water (F-).
- Some benefits of chlorinated drinking water:
- Chlorinated drinking water is protected from bacterial infestations even after it leaves the plant.
- Chlorinated drinking water helps prevent many illnesses that could be extremely harmful to humans and other organisms.
- A disadvantage to using chlorination in water treatement is that sometimes Cl in water reacts with natural organisms that are produced by decomposing mammal or plant matter to produce trihalomethanes (THMs); one well-known THM is called chloroform and it is a carcinogenic to humans.
- Water from a clear mountain stream still needs to be processed because either it may contain small particles of human waste or it may contain substances in water that may have been added as the slightly acidic water ran through water with soluble substances like magnesium.
- Two alternitaves of water chlorination are using ozone or UV light.
- If Earth’s hydrologic cycle would not exist if water evaporation suddenly stopped because there would be no way for clouds to accumulate and without cloud formation there would be no rain; therefore, without evaporation the world would not have a replenishing source of fresh water.
- If water could not be present in all three stages (gas, liquid, and solid) with normal Earth temperatures the hydrologic cycle would not be even relatively similar to the cycle Earth now possesses; without evaporation of water molecules the hydrologic cycle would not be able to perform its function.
- The EPA limits the concentration of THMs to 80ppb instead of requiring their total elimination because there is no way to acquire their total elimination from the water without discontinuing the use of chlorine; therefore, until we find alternate ways of purifying water THMs will always be present.
- Some steps from the water purification lab that are similar to steps in the natural purification include:
- Sand filtration- sand filtration, though used for the foul-water lab, is also a natural way to filter big particles out of water.
- Distillation- The distillation apperatice evaporates water in order to separate out the unwanted particles that were too small to filter out. Natural evaporation does the same thing and then condenses the water into clouds.
- Assume that you drink 2 L of water per day. At 1 ppm fluoride, how many grams of fluoride ion would you consume in
- One day- 1gF/1,000,000,000 x 2L/1 day x 1,000mg/1g x 1 day = 2mg F
- One week- 14 milligrams of fluoride per week
- One year- 730 milligrams of fluoride per week
Percent concentrations
Percent concentrations
A percent concentration refers to the percent of solute that is dissolved in a specific quantity of solvent or solution. Percent means parts solute per hundred total parts (solute plus solvent) so 5% salt solution could also be reported as a five parts per hundred salt solution (5pph) but percent is more commonly used. When solutions contain very small quantities of a solute concentration units of parts per million (ppm) and parts per billion (ppb) are useful because instead of writing (for ppm) .0005 one can write 5 ppm.
How to calculate percent concentrations
Example problems:
1.A common salt water solution contains 30 grams of table salt and 60 grams of water what is the concentration of this solution expressed in percent by mass?
First one places 30g over 60 plus 30 (30g/60+30) then add 60 + 30 (30g/90g) then divide 30 by 90 and you will get .33 then you multiple .33 by 100 (.33x100) and you will get 33% of salt.
2. Lets say there is 33% of salt in 90gs of a salt-water solution how many grams of salt are there?
First you divide 33% by 100 and get .33 then you multiple .33 by 90 and get 30 grams of salt.
3. When transferring a number into parts per million or parts per billion you take the number (usually in decimal form) and move the decimals all the way to the right.
Examples:
.0005 = 5 ppm and .00005 = 5ppb.
4. In order to transfer a number back from when it is converted to ppm (for ppb one must divide by 1 billion) one must divide that number by 1,000,000 then multiply by the amount of g of solvent present
Example: Lets say there are 5ppm of salt in 100g of water how many grams of salt are there present in the water?
5ppm/1,000,000 = 0.000005 x 100 = 0.0005 grams of salt are present in 100 grams of water
Monday, June 27, 2011
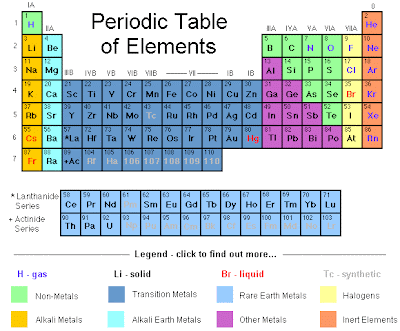
The Periodic Table of Elements
Scientists all around the world use the periodic table, it has three groups the metals, metalloids, and non-metals usually color-coded. The elements in the periodic table want to be chemically stable like the noble gases; therefore, elements form ions by losing or gaining electrons. The elements tend to lose or gain electrons in order to be like the elements that lay directly across the table. The elements that lose electrons become positive ions and visa versa for the elements that lose electrons. Each element on the periodic table has a different atomic symbol, atomic number, and atomic weight. The atomic symbol tells one how many neutrons and electrons that element has, the atomic weight tells the atomic mass of the element, and the atomic symbol shows what element it is.
Homework #1 week three
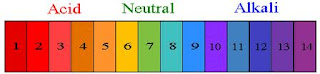
- Using figure 1.44 on page 70, decide which is more acidic:
- A soft drink or a tomato- A soft drink is more acidic with a pH of 3
- Black coffee or pure water- Black coffee is more acidic with a pH of 5
- Milk of magnesia or household ammonia- though both are considered basic milk of magnesia is more acidic with a pH of 10.
- A solution at 2.0 pH is 100 times more acidic then a pH of 4.0
- Three negative affects of inappropriate pH levels on aquatic organisms: low pH (highly acidic) impair fish egg development, also low pH increases the concentration of metal ions in natural waters that are toxic to fish in high concentration, and alkaline solutions are harmful because they are able to dissolve organic materials like skin and scales.
- Polar molecules have an uneven distribution of electrical charges usually with a negative charge on one end and a positive charge on the other and dissolve in polar solvents; non-polar molecules only dissolve in non-polar solvents.
- I would select lamp oil and ethanol to dissolve and non-polar molecule because non-polar molecules dissolve in non-polar solvents such as oil.
- Table salt dissolves in water because it is a polar solute and it does not dissolve in oil because oil is a non-polar solvent.
- The phrase “like dissolves like” refers to the patter in which polar molecules dissolve in polar solvents only and non-polar solutes dissolve in non-polar solvents only.
- A person cannot satisfactorily clean greasy dishes with just plain water because greasy is a non-polar solute and water is a polar solvent; therefore, the grease cannot dissolve or be cleaned with just plain water.
Sunday, June 26, 2011
Homework #5 week two
- .20 x 55.0 = 11grams of sugar 44 grams of water
- 0.015mg/L = 150 ppm
- A water molecule is polar because it has a negative charge on one side (the oxygen side) and a positive charge on the other side (the hydrogen side).
- On paper
- The region of polar water molecules that will be attracted to a
- K+ ion is the negative oxygen side
- Br- ion is the positive hydrogen side
- Heavy metals are called heavy because their atoms have bigger masses than the other essential metal elements; they are harmful to humans and other organisms because they bind to proteins in biological systems and prevent the proteins from doing their jobs.
- Three symptoms of heavy metal poisoning: nervous system damage, kidney failure, and brain damage.
- Two possible sources of human exposure to
- Lead- Through old gasoline fumes, which used to contain tetraethyl lead, and through flaking paint from houses that were built in the 70s or earlier.
- Mercury- Through mercury vapor from a cracked fluorescent light, which is extremely harmful; mercury is used because it is a great electrical conductor. Another source of human exposure to mercury is through a broken mercury thermometer.
- The ion found in many bases is hydroxide (OH-) and the bases that do not have hydroxide in them usually produce the ion when they react with water.
- The element found in most acids is hydrogen (H) that can be released very easily in water solution.
- Classify each sample as acidic, basic, or chemically neutral:
- Seawater with a pH = to 8.6 is basic
- Drain cleaner with a pH = to 13.0 is extremely basic
- Vinegar with a pH = to 2.7 is very acidic
- Pure water with a pH = to 7.0 is neutral
Thursday, June 23, 2011
Homework #4 Week Two
- A person would see a separation between the water and the torn crystal ions in the solution when cooled.
- The amount of water that must evaporate at 40 C to create a saturated solution is 50g
- 55 g for b ii.
- The key feature that is different between my two models is that the second one barely has any solute because the solvent over powers it.
The rest are on paper
"The Difference Engine: The Spy in Your Pocket" Extra credit week two
Cell phones, used constantly throughout the day may be doing more than just sending a text to your friend. According to “The Difference Engine: The Spy in Your Pocket” Apple and Google phones like the iPhone and the Droid are tracking the locations of every cell phone around the country. Two British researchers stumbled across Apple’s location database in which Apple had been storing the location data from all the cell phones around the country; the iPhones recorded the data when synced to computers and every time the phones were used. However, when confronted with this issue Steve Jobs Apple’s CEO denied that the Apple had been tracking locations and stated that the location data was coming from their service towers instead. Even though Apple said that they were not collecting data and that no problem existed, they stated the privacy issues were going to be fixed so that no one could obtain the information. However, a large quantity of the information found in the data bases were locations that were used to help gpses on both the Google phones and Apple phones, but the over use of the cell phone location data became the main problem. Mainly the reasons that people became upset over the fact that the data was collected were because Apple had been secretly reporting the information back to its headquarters and collecting data even when people turned off their location services. Therefore, people became concerned with the fact that their phones were tracking their location multiple times a day. However, this is both a blessing and a curse because sometime in the future the cell phone companies could use the locations to suggest certain restaurants or stores that a person is near or send them coupons to save money; the part of the equation that is debatable is that cell phone companies are selling the locations and information in order to gain money from telemarketers that own stores or restaurants in the recorded location. Though the collection of data may seem like an invasion of privacy in some cases it could be convenient for the cell phone users; However, for the time being the data needs to be more thoroughly protected and cell phone users should be informed that their locations are being recorded.
Corrected Hw #3 week two
Homework #9 p 56 and p 82
-
- The mass of potassium nitrate that will dissolve in 100 g water at the same (60 C) is 105 g.
- the mass of potassium nitrate that will dissolve in 100 g of water at 60 degrees C is 45g.
-
- The amount of potassium nitrate in grams that must be added to form a saturated solution at 30 C is 20 g.
- The minimum mass of 30 C water needed to dissolve 25 g potassium
25g/ xg=45gKNO3/ 100g xtimes 45g/45= 2500g/45= 56.
-
- If the solution is agitated 150-95= 55 g of potassium nitrate will precipitate.
- 150gKNO3/ x gwater= 95g KNO3/l00g water = 95x/95= 1500/95 x= 160g-100g= 160g
- Three teaspoons of sugar will completely dissolve in hot tea because water can become saturated when heated; therefore, more sugar can dissolve when the tea is heated while barely any can dissolve in iced tea.
- The maximum mass of potassium chloride that will dissolve in 100g of water at 70 C is 48 g.
-
- If the solubility of sugar in water is 2.0 g/mL at room temp, the maximum mass of sugar that will dissolve in 100.0 mL of water is 200g/ mL.
- The maximum mass of sugar that will dissolve in 355 mL of water 355 as much solvent so 355 x 2g = 710g.
- The maximum mass of sugar that will dissolve in 946 mL of water is 946x 2g = 1,892g
-
- At 20 C: NaCl, KCI, KNO3
- At 80 C: KNO3 ,NaCl, KCI
- Saturated means that a substance has reached its full solubility while unsaturated means that the substance has not reached its solubility level and more solute can be added.
-
- The maximum mass of KNO3 that can dissolve in 100 g of water at 20 C is 31 g.
- At 30 C, 55 g KNO3 is dissolved in 100 g water. The solution is unsaturated because in 100 g of water KNO3 can hold 80g when fully saturated.
- 80g of solid KNO3 should precipitate as the saturated solution cools from 75 C to 40 C.
-
- When you add a crystal to an unsaturated solution of KNO3 the crystal will eventually dissolve.
- When you add a crystal to a supersaturated solution of KNO3 the rest of the solutes will fall out of the solution again forming crystals and sinking to the bottom; it will rebalance its self
- When you add a crystal to a saturated solution of KNO3 the crystal will not dissolve unless heated.
- 23% concentration of ethanol is dissolved in 115g of water.
35g of ethanol/ 115+35g of ethanol X 100%= 23 %
Wednesday, June 22, 2011
Blog question
For review look at:
Math problems
-unit conversions
-metric systems
chemical formulas
substances mixture and more
Ions
Element symbols
pH
Vocab
Drawings
Homework #3 week two
-
- The mass of potassium nitrate that will dissolve in 100 g water at the same (60 C) is 100 g.
- the mass of potassium nitrate that will dissolve in 100 g of water at 69 degrees C is 45g.
-
- The amount of potassium nitrate in grams that must be added to form a saturated solution at 30 C is 50 g.
- The minimum mass of 30 C water needed to dissolve 25 g potassium nitrate is 50 g of water.
-
- If the solution is agitated 70 g of potassium nitrate will precipitate.
- 25 C would have to be added in order for the potassium nitrate to dissolve completely
- Three teaspoons of sugar will completely dissolve in hot tea because water can become supersaturated when heated; therefore, more sugar can dissolve when the tea is heated while barely any can dissolve in iced tea.
- The maximum mass of potassium chloride that will dissolve in 100g of water at 70 C is 50 g.
-
-
- mass of sugar that will dissolve in 100.0 mL of water is 200g/ mL.
- The maximum mass of sugar that will dissolve in 355 mL of water 355 as much solvent so 355 x 2g = 710g.
- The maximum mass of sugar that will dissolve in 946 mL of water is 946x 2g = 1892g
-
- At 20 C: KNO3, KCI, NaCl
- At 80 C: NaCl, KCI, KNO3
- Saturated means that a substance has reached its full solubility while unsaturated means that the substance has not reached its solubility level and more solute can be added.
-
- The maximum mass of KNO3 that can dissolve in 100 g of water at 20 C is 30 g.
- At 30 C, 55 g KNO3 is dissolved in 100 g water. The solution is unsaturated because in 100 g of water KNO3 can hold 80g when fully saturated.
- 80g of solid KNO3 should precipitate as the saturated solution cools from 75 C to 40 C.
-
- When u add a crystal to an unsaturated solution of KNO3 the crystal will eventually evaporate.
- When you add a crystal to a supersaturated solution of KNO3 the rest of the solutes will fall out of the solution again forming crystals and sinking to the bottom.
- When you add a crystal to a saturated solution of KNO3 the crystal will not dissolve.
- 30.4 % concentration of ethanol is dissolved in 115g of water.
Tuesday, June 21, 2011
Water testing Lab report
Katrina Cymerman
Chemistry
Dr. Forman
06/21/11
Lab Report for the Water Testing Lab
Abstract- For the Water testing lab we needed to test each substance for the presence of Calcium Ion, Iron Ion, Chloride Ion, and Sulfate Ion. We tested for each substance by placing at least three drops of different solute for each test. For the Calcium Ion we needed to use sodium carbonate in order to detect whether there were traces of the ion in the water. To test for Iron we used potassium thiocyanate and only had results in the control and reference. The reaction caused an almost blood red color and solids to form. For the Chloride ion test wee used silver nitrate, which was a dangerous substance and needed hand protection, and we found reactions in ocean water, control, and reference. Then for the Sulfate ion we used barium chloride in order to get a reaction in the distilled water, ocean water, reference, control, and tap water. In each test we found the impurities in water; therefore, the tests were successful.
Procedure- Obtain materials: ocean water, control, bottled water, silver nitrate, Barium chloride solution, calcium chloride solution, ferric initrate solution, ferris solfate solution, potassium thyocyanate solution, well plate, stir rod, tape (to label). For the Calcium Ion (Ca2+ ) test we added 20 drops of distilled water in the first dip, labeled it, and then put the put three drops of sodium carbonate directly afterwards. After the distilled water observations we place 20 drops of the control liquid in the second dip and labeled it control, and then we dropped 3 drops of the sodium carbonate into that. After observing and writing down the reaction to the control we dropped 20 drops of the calcium chloride (Ca2+ ) reference solution into the third dip and dropped three drops of the sodium carbonate. Then we put 20 drops of ocean water into the fourth dip and put 3 drops of sodium carbonate into the solution and observed and after we did the same process to the tap water. After cleaning out the well plate my group started working on the iron test. For the Iron (III) ion (FE 3+) water test we used the same materials and repeated the same procedures. In the first dip we placed 21 drops of distilled water (one accidentally drop), in the second dip we placed 20 drops of the control, in the third dip we placed 20 drops of the ocean water, in the fourth dip we placed 20 drop of the Iron reference, which was ferric nitrate and we got confused on weather to use feriss solfate or the ferric nitrate and put 20 drops of the feriss solfate into a dip in the second column; in the second dip on the second column we put 20 drops of tap water. After placing all the solutions with the correct labeling and with the correct amount we put 3 drops of potassium thiocyanate into each dip in the well plate and observed and documented the results. After we had finished the Iron testing we cleaned out the well plate again and began to work on the next test. The Chloride ion test was the next test in the instructions. We placed 20 drops of distilled water into the first dip and put 3 drops of silver nitrate into the solution then we placed 20 drops of the control into the second dip and added 3 drops of the silver nitrate; we placed then placed ocean water into the third dip and put 3 drops of silver nitrate, and we dropped 20 drops of the reference which was calcium chloride into the fourth dip and put 3 drops of the silver nitrate into that solution and observed and documented the reaction. Finally we placed 20 drops of tap water into the second dip on the second column and dropped 5 (accidentally added 2 more) drops of silver nitrate into the solution and observed and documented any occurrence. Finally, after re-rinsing the well plate, we began our last test, which was Sulfate Ion (SO2- ). We placed 20 drops of the distilled water into the first dip, then we put 20 drops of the control into the second dip, 20 drops of ocean water were added to the third dip, 20 drops of the reference, which was feriss solfate were added to the fourth dip, and finally 20 drops of tap water were added to the second dip on the second column. After adding 3 drops of the Barium chloride to each solution we recorded the results and clean our station and supplies. Also for most of the time we wore gloves to protect our hands again the chemicals.
Results- For the first test, the Calcium Ion (Ca2+ ) test, our results were interesting. In the distilled water nothing seemed to happen and no precipitate was present nor was there a color change, yet in the control we observed that a precipitate was formed and it looked cloudy. In the ocean water very small precipitates formed and the water looked cloudy and in the reference precipitate was formed and made the appearance cloudy as well. Finally in the tap water after adding the sodium carbonate only very tiny precipitate formed. The reason the reactions occurred was because there was traces of Calcium Ions in some of the substances. For the Iron test when potassium thiocyanate was added to distilled water nothing happened; however, when added to the control and reference, the solutions changed to deep reds and precipitate was formed in both. When added to the ocean water nothing happened and when added to the tap water nothing happened. Each reaction happened because there was some type of trace or presence of Iron ions in the reacting substances. For the Chloride Ion test the distilled water had no reaction to the silver nitrate, the control had a big reaction with a color change to white and precipitate formation, the ocean water had big precipitates and pure white color, the reference changed to a pure white color with large precipitates as well, and the tap water, after an accidental addition of two drops over three, nothing happened. These reactions happened because there was some trace of chloride ions inside the solutions that had reactions. In the Sulfate Ion (SO2- ) test the results after addition of the barium chloride were: for the distilled water a little bit of white appeared and made the substance cloudy, in the control there was precipitate and it was very cloudy white color, in the ocean water there was precipitate and cloudiness of the substance, in the reference the color was white and precipitates were formed, and in the tap water there was a small reaction with very small precipitates. Each reaction occurred because there was a trace or presence of Sulfate Ions in the substances that had a reaction. The results were all different and some were unexpected.
Questions-
- A reference solution and blank were used in order to see the difference between a reaction and a non-reaction.
- Some possible problems associated with the use of qualitative tests could be that they only tell whether there is a presence or an absence of a substance not the amount, which can cause issues because some elements that are in water are needed in very small amounts; however, the elements could become to large of a presence in the water and cause more damage that help.
- The tests cannot absolutely confirm the absence of an ion because there is no way to exact test for an absence of a substance; scientists just need to use deductive reasoning to figure out what ions are in the water.
- The observations would have changed if my group hadn’t cleaned out our tools thoroughly because we could have contaminated our samples and observed false positives instead of the actual results.
Data tables
Homework #2 week two
- The main difference between qualitative and quantitative is that qualitative tests just exhibit whether there is a presence of a substance or not while quantitative shows the amount of the substance present.
- Confirming tests confirm that the ion in question is present.
- A. The purpose of a reference solution is to show how the substance is supposed to react if the ion in question is present. B. The purpose of the distilled-water blank is to exhibit what a substance that does not react is supposed to look like.
- The student should not conclude that there is no iron present because there is no possible way to disprove an ions presence with the water testing method used in the lab.
- A. When given an unknown mixture I would determine whether it was a sollution, suspension, or colloid by trying the Tyndall effect, stirring to see if the substance changes in any way, and filtering to see if any particles are big enough to be filtered. B. The Tyndall effect shows that the substance is not a solution; if the substance is changed by stirring it cannot be a solution, and if the subsance can be filtered it is not a solution.
- The possible risks in failing to “shake before using” are that the medicine could not be mixed properly and could not be helpful to the sick person.
- It is useful for element symbols to be universal in science because unlike the metric system vs. the SI system there would be no conversions necessary; therefore, scientists would have an easier job distributing their discoveries universally.
- No it is not possible for water to be 100% chemical free because the The atmospheric gases such as nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide dissolve into the water deeming it impure.
- The physical properties of water are different from the physical properties of the elements it is made of. Water is made of 2 Hydrogen gas molecules and 1 oxygen gas molecule; these two elements are in a gaseous state at room temperature while water is in a liquid state at room temperature. Also, the freezing, boiling and liquid states of these gases are very different from water and the surface tension is less for the gases then for water.
What I learned from the water testing
What I learned from the water-testing lab is that many different ions that are not visible to the naked eye are very present in our water. Some results with tap water surprised me as well because I did not expect to get any results for those ions. The lab really helped me understand how water can be contaminated and really supports my theory that water pollution is worse than lack of water because the water may look clear and pure but in reality no water can ever be completely pure.
Monday, June 20, 2011
How does testing water help us?
Testing water helps people observe any unwanted chemicals or elements that may have found their way into our water supply. With specific tests geared towards any unwanted ions in the water people can see what the problem is with their water. For example in the text book Riverwood needs to perform water tests in order to figure out why all the fish in their lake have suddenly died. Water tests are a good way to figure out some issues with water that may not be visible with a naked eye.
Homework #1 week two part two
19. a. carbon 6 protons and 6 electrons
b. aluminum 13 protons 13 electrons
c. lead 82 protons 82 electrons
d. chlorine 17 protons 17 electrons
20. a. sulfur 16 protons 18 electrons Not balanced
b. iron: 26 protons 24 electrons Not balanced
c. Silver: 47 protons and 47 electrons Balanced
d. Iodine: 53 protons and 54 electrons Not Balanced
21. a. anion
b. electrically neutral
c. electrically neutral
d. cation
e. cation
22. a. for O2- from gaining an electron
b. Li is neutral so neither
c. Cl is neutral so neither
d. Ag+ from losing an electron
e. Hg2+ is from losing an electron
23. a. H neutral
b. Na+
c. Cl-
d. Al+
Homework #1 week two
- 1,939.2 L was used during the three days of the water diary
- 216 L was used per person on average each day.
4. The range of the class per person is 734L.
5. 446.9 L for the average in the class per person and the median for the class is 472 L the better representative would be the mean of 446 because the average for the U.S. is 370 L and 446L is closer than 472L.
6. My class is over the average number per person daily because many of the homes happen to be bigger than the average home. Therefore, there are more bathrooms, pools, and bigger yards.
7. My answer for question 2 (216) is closer to the national average because the national average is lower than the class mean which is higher than the average for the U.S.
Sunday, June 19, 2011
Friday, June 17, 2011
Homework #5 week one
- Two pieces of information that a chemical formula tells people are the number of atoms of the element and each element present.A. Number four; two, one, and five represent elements. B. Numbers three and six represent compounds.
- A. 3 hydrogen, 1 phosphorous and four oxygen. B. 1 salt, one oxygen, and 1 hydrogen. C. 1 sulfur 2 oxygen
- C. Hydrogen reacts with two chlorines to form a hydrogen chlorine product. Four hydrogen and four oxygen react to form 4 hydrogen attached to 2 oxygen plus two oxygen.
- NaHCO3 + HCI
 NaCl + H2O + CO2 ; C6H12O6 + O6
NaCl + H2O + CO2 ; C6H12O6 + O6 6CO2 + 6H2O.
6CO2 + 6H2O.
Thursday, June 16, 2011
Summary
Water, the most valuable source of life on our Earth and one of the most rare liquids in out universe, is being polluted everyday by human artifacts. Plastic is one of the main pollutants in the world and one of the most harmful especially in the oceans. “A New Year’s Wish for less trash” is a vivid article on how trash is affecting the Earth’s oceans. According to the article plastic is extremely harmful and dangerous in our oceans because it not only attracts chemicals like DDT and PCBs but it can choke animals or even end up in our food supply. Also there are multiple islands of pure non-biodegradable trash that are mostly made of plastic; the largest island happens to be right off the coast of California. The Great Pacific Garbage Patch also known as the plastic graveyard is about 500 miles away from the coast of California and is as large as the continental U.S. Unfortunately, there are different garbage patches found in all of Earth’s oceans, which are contaminating the water and leading many scientists and environmentalists to worry that plastics will become an even bigger issue as more of the substance is created. Hopefully many people will become more conscious about their plastic use and learn to use less. According to the article 100m tons of plastic will be created next year and a lot of that amount will end up in our oceans. In order to not pollute many people should begin limiting their plastic use and really think about buying new plastic products. The pollution of water is very dangerous for animals, the Earth, and human beings.
http://www.economist.com/blogs/babbage/2010/12/ocean_pollution
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)